Newsroom
Program Areas
-
Google Continues Big Data-Driven Tracking and Analyzing of Individuals for Cross-Device Targeting
Presented by the Google Agency blog "Introducing Ads Data Hub: Next generation insights and reporting"
Mobile has fundamentally changed how we live our lives. With our devices never more than an arm’s length away, people can find, watch or buy anything at anytime. That’s why earlier this year we shared (link is external) that we’re developing a new, cloud-based measurement solution for YouTube, designed for a mobile world. Today, we’re announcing the beta for this solution, Ads Data Hub, to help advertisers get more detailed insights from their campaigns across screens while also protecting user privacy. We are also announcing that Ads Data Hub is a solution not just for YouTube, but a tool that offers access to more data and helps unlock actionable insights across Google ad platforms, including the Google Display Network and DoubleClick. And with Ads Data Hub now in beta, we’re expanding who can use it. Built on infrastructure from Google Cloud, including BigQuery (link is external), Ads Data Hub gives advertisers or their preferred measurement partners access to detailed, impression-level data about their media campaigns across devices in a secure, privacy-safe environment. Data from other sources, such as a CRM system or marketing database, can be incorporated as well. With this full view, advertisers or their partners can analyze the data and draw out insights specific to their business. For example, if an e-commerce retailer wants to understand what the path to conversion looks like, they can bring additional online data about their customers into BigQuery, and Ads Data Hub will enable them to combine that data with their ads data so they can see what a typical journey is from first encountering a user until conversion. Consistent with our commitment to privacy (link is external), no user-level data can be removed from the secure Cloud environment. Impression-level data is only accessible for the purposes of analysis and generating insights. In the future, advertisers will be able to act on the insights they get from Ads Data Hub and buy media with greater precision. As an early alpha partner, Omnicom Media Group helped to define the solution and has seen significant value from both the amount of data available through Ads Data Hub and the broad set of analyses and custom queries that are possible. --- For the full blog post, visit http://bit.ly/2yBWYv1 (link is external) -
Press Release
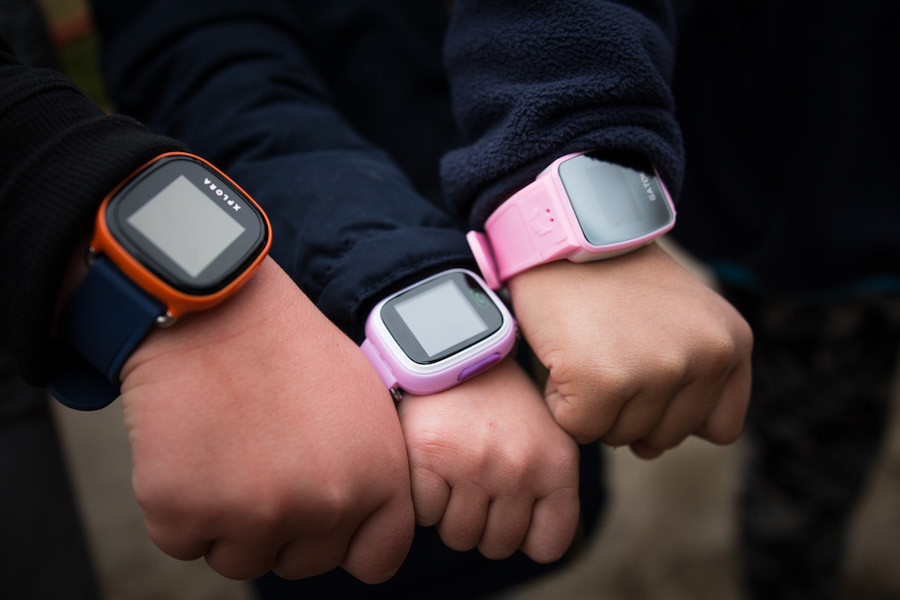
“Smartwatches” For Parents to Monitor Young Children Actually Pose a Danger to Kids’ Welfare—Report
Groups call for investigation and action by U.S. and EU Regulators, including FTC
WASHINGTON, DC – October 18, 2017—A number of brands of “smartwatches” intended to help parents monitor and protect young children have major security and privacy flaws which could endanger the children wearing them. A coalition of leading U.S. child advocacy, consumer, and privacy groups sent a letter to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) today, asking the agency to investigate the threat these watches pose to children. Smartwatches for children essentially work as a wearable smartphone. Parents can communicate with their child through the mobile phone function and track the child’s location via an app. Some product listings recommend them for children as young as three years old. Groups sending the letter to the FTC are the Electronic Privacy Information Center (EPIC), the Center for Digital Democracy (CDD), the Campaign for a Commercial-Free Childhood (CCFC), the Consumer Federation of America, Consumers Union, Public Citizen, and U.S. PIRG. The advocacy groups are working with the Norwegian Consumer Council (NCC), which conducted research (link is external) showing that watches sold in the U.S. under the brands Caref and SeTracker have significant security flaws, unreliable safety features, and policies which lack consumer privacy protections. In the EU, groups are filing complaints in Belgium, Denmark, the Netherlands, Sweden, Germany, the UK, and with other European regulators. “By preying upon parents’ desire to keep children safe and, these smart watches are actually putting kids in danger,” said CCFC’s Executive Director Josh Golin. “Once again, we see Internet of Things products for kids being rushed to market with no regard for how they will protect children’s sensitive information. Parents should avoid these watches and all internetconnected devices designed for kids.” The NCC’s research showed that with two of the watches, a stranger can take control of the watch with a few simple steps, allowing them to eavesdrop on conversations the child is having with others, track and communicate with the child, and access stored data about the child’s location. The data is transmitted and stored without encryption. The watches are also unreliable: a geo-fencing feature meant to notify parents when a child leaves a specified area, as well as an “SOS” function alerting parents when a child is in distress, simply do not work. The manufacturers’ data practices also put children at risk. Some devices have no privacy policies at all, and the policies that do exist lack basic consumer protections, including seeking consent for data collection, notifying users of changes in terms, and allowing users to delete stored data. "The Trump Administration and the Congress must bring America’s consumer product safety rules into the 21st century,” said Jeff Chester of the Center for Digital Democracy. “In the rush to make money off of kids’ connected digital devices, manufacturers and retailers are failing to ensure these products are truly safe. In today’s connected world that means protecting the privacy and security of the consumer—especially of children. Both the FTC and the Consumer Product Safety Commission must be given the power to regulate the rapidly growing Internet of Things marketplace.” The Caref (branded Gator in Europe) and SeTracker smartwatches are available online through Amazon. The groups have asked the FTC to act quickly to investigate these products, and they advise parents to refrain from buying the products because of the danger they could pose to children. The NCC, which conducted the testing of the watches, advises consumers who have already purchased the watches to stop using them and uninstall the app. “The Federal Trade Commission must be proactive in protecting consumers—especially vulnerable young children—from harmful products that abuse technology for the sake of profit,” said Kristen Strader, Campaign Coordinator for Public Citizen. “Smartwatches and similar devices must be absolutely safe and secure before they are released to the public for sale.” Ed Mierzwinski, Consumer Program Director at U.S. PIRG, said, "Companies making any internet-connected devices, but especially for children, need to ensure that privacy and security are more than breakable — or worse, hackable — promises." Katie McInnis, technology policy counsel for Consumers Union, said, “When a company sells a smartwatch aimed at children, it must ensure the product is safe and secure. The FTC should launch an investigation into the privacy and security concerns surrounding these products to make sure families are safe.” The same trans-Atlantic coalition persuaded government authorities and retailers last December (link is external) that the internet-connected dolls Cayla and i-Que Robot were spying on children and threatening their welfare, and retailers removed the toys from store shelves. The FBI subsequently issued a warning to consumers (link is external) that internet-connected toys could put the privacy and safety of children at risk. --- For more information, please see the following: Letter to FTC by coalition of leading U.S. child advocacy, consumer, and privacy groups (link below) Press Release by US coalition of leading U.S. child advocacy, consumer and privacy groups (link below) #WatchOut Report by Norwegian Consumer Council (link below) Press Release by Norwegian Consumer Council (link below) #WatchOut English - YouTube (http://bit.ly/2ghNoD1 (link is external)) #WatchOut - longer video explainer on security flaws 4:30 mins - YouTube (http://bit.ly/2xLYSVv (link is external)) -
Digital Data Targeting of Political Ads Require 21st Century Voting Safeguards, inc. for Privacy
Here’s what Verizon does:
'One by AOL: Politics', a full-scale programmatic solution that inspires voters at the "right time", in the "right context" in an increasingly video and mobile-led world. Use of this platform allows political brands to create, execute and optimize on digital buys to reach voters. --- For more information, visit https://www.onebyaol.com/politics (link is external) -
Google + Ad Industry Study Shows Influencers on YouTube Sell Snacks, Toys, Alcohol
Illustrates Need for 21st Consumer Safeguards for Unfair/Deceptive Marketing
Sanjay Nazerali, Chief Strategist of Carat, a global media market leader in digital media, writes about how YouTube influencers are rewriting the marketing rulebook. Working in strategy at one of the world’s largest media agencies, I’ve witnessed countless pitches about influencer marketing and the growing power of creators. With engaged audiences in the millions and passionate fans hungry for content, YouTube creators are already an established channel for brands looking to run ads. In fact, Carat’s latest analysis suggests online video investment (including YouTube) can be increased by 3X compared to planned level. But increasingly, these influencers are also becoming attractive partners for deeper collaborations. Clients are initially enthusiastic, assuming this is the digital age’s answer to celebrity marketing and endorsement. Then the thorny business questions arise, such as: So what’s it actually doing for my brand? Do I do an endorsement or product placement—or what? Isn’t it just for millennials, beauty brands, and makeup tutorials? These have always been tough questions to answer. Even though almost everyone has been jumping on the influencer bandwagon, few understand what “influence” really is or how it works. Until now. Celebrity marketing and influencer marketing offer fundamentally different benefits for brands. Together with YouTube and Nielsen, my team analyzed the results of hundreds of brand and creator videos in the U.S. and the U.K to understand the impact of influencers for brands. It’s a critical first step in establishing a business-led rulebook for this new world—and it’s already changing how I approach my own plans. 1. Influencers are not the same as celebrities Influencers, however vast their reach, are absolutely not “today’s celebrities,” and celebrity marketing and influencer marketing offer fundamentally different benefits for brands. For instance, we found that celebrities are more effective at driving recall than creators (84% versus 73%). Given that a celebrity’s job is to be famous and memorable, that makes sense. Where YouTube creators really start to gain the upper hand is in deeper brand involvement. Brand familiarity is a good example. If we want to get an audience to really understand us, our work, our values, or our products, then collaborations with YouTube creators are 4X more effective at driving lift in brand familiarity than those with celebrities. When it comes to purchase intent, it’s an even match: our research found that influencers were just as likely as celebrities to drive buying decisions. Influencer marketing appears to play a fundamentally more pragmatic role. Why? My hunch is that it’s because fans feel very connected to the YouTubers they love. The best creators have formed authentic bonds with their fans, which means fans trust what they have to say, and turn to them for brand and product recommendations. 2. It’s not just a ‘beauty’ thing Beauty brands were one of the first to team up with influencers, and creators have established a huge presence among the YouTube beauty community. About 86% of the top 200 beauty videos on YouTube were made by creators rather than professionals or brands. But what’s interesting about our findings is just how far influencers stretch beyond the beauty category. We tested nine additional categories, including auto, alcohol, snacks, and toys. Across all nine categories, working with influencers leads to lifts in brand metrics, from familiarity to affinity to recommendation. In some categories, such as snacks and alcohol, they can have even more impact, driving significantly higher than average purchase intent. So the idea that influencer marketing is purely for young people who are looking at fashion and beauty brands simply isn’t true. 3. The ‘how’ matters as much as the ‘who’ Celebrity marketing has historically focused on endorsement, sponsorship, and product placement. Influencer marketing has developed far more options, and it’s important to understand which of these work best—and for which marketing goals. Deep thematic integrations with creators stand out as driving the highest results for brands. These are more involved integrations where the influencer plays a role in creating a piece of content – such as a demo – with the brand. It’s far deeper than product placement and it works more effectively. While there were many consistencies across categories, we also saw some nuances, which are important for clients to understand. We found that simpler brand integrations, like a product endorsement or just featuring a creator in an ad, also showed positive results for brand affinity in all categories tested. Of course, deep collaborations can be more than some brands are ready for. For some objectives and categories, simply running their own ads on YouTube creator content will still be the easiest and most effective way to tap into the power of these influencers. 4. Don’t lose sight of why people love YouTubers We often assume that the right influencer is either an aspirational version of our target audience or that they’re just like celebrities. Neither of these assumptions is correct, and it’s perhaps here that celebrity and influencer marketing differ the most. Whereas celebrities need to be trendy and stylish, consumers expect creators to be friendly, funny, and, yes, sometimes irreverent. Irreverence is interesting, because it drives credibility. Irreverence strongly suggests independence, and it’s this that builds trust. It can also be incredibly valuable for brands. If a creator usually ridicules things they don’t like, you can be sure that when they praise something, they mean it. Humour is also interesting, because it reflects a sense of community. YouTube helps forge a special relationship between followers and influencers, one that reflects a sense of co-ownership. This familiarity creates a degree of intimacy that makes the use of humour seem much more natural than it would do with celebrities. This is probably also why we see celebrities, such as Dwayne Johnson, increase their influencer scores when they get really active on YouTube. Prioritization and strength of attributes by gen X and gen Y associated with celebrities are different to creators. --- For the full article, visit http://bit.ly/2z6MHng (link is external) Is it Hype? Or is it Real? Decoding the Influence of YouTube Influencers Read more at http://newyork.advertisingweek.com/CALENDAR/-google-seminar-2017-09-26-1... (link is external) -
Leading radio streaming service Pandora partners with Oracle Data Cloud (link is external) on two important measurement initiatives: a custom offline sales meta-test of consumer packaged goods (CPG) campaigns and automotive Buy Through Rate (BTR) measurement. Connecting online ad exposure to offline sales requires billions of data points. Massive scale is crucial. With more than 76 million logged-in listeners per month, 1 billion data signals every day, and cross-platform reach, Pandora is uniquely positioned to provide our advertisers with the crucial data they need. In both the CPG and Auto studies, Pandora‘s listener data was matched anonymously, one-to-one with Oracle Data Cloud user-level data set. Pandora’s cross-platform media was then connected with offline transactional consumer data from the Oracle Data Cloud. For marketers, being able to accurately measure a campaign’s impact on in-store sales truly is the holy grail. With 67% of the buyer’s journey (link is external) happening online, digital marketing has never been more directly connected to offline sales. It’s also the thing that keeps marketers awake at night and a challenge that here at Pandora, we’ve taken to heart. Campaign-level sales insights are equally important for automotive marketers as their CPG counterparts. Yet, auto purchase cycles are even longer and more complex, making sales attribution a struggle. Pandora is proud to lead the charge in this space and is the first non-endemic publisher to leverage Oracle Data Cloud Buy Through Rate at a raw impression/user level, exposing detailed and granular campaign-level insights. --- For more information, visit http://bit.ly/2g3Ic5u (link is external)
-
Learn more about Krux’s data management platform solution ‘marrying human insight and machine learning’. People are unique, from their different characteristics to preferences to behaviors. People engage with brands in infinitely different ways, and they certainly don't fit neatly into standard audience personas. More granular and dynamic audience segments can be discovered and defined through Salesforce DMP machine learning capabilities powered by Einstein. Salesforce DMP Machine-Discovered Segments deliver: Machine-learning algorithms that detect similarity and correlation between users to find hidden patterns and behaviors Prescriptive audience recommendations based on all data sources Unique audience personas that differentiate and augment the value of your first-party data Intelligently targeted and personalized engagement Complete analysis and actionable data to discover, activate, and measure Key Features include: Programmatic Attribution Modeling: Smart insights for smart ad buys and activation across all screens, channels and systems. Turnkey Lookalike Modeling: Audience expansion in which you control the tradeoff between reach and similarity, without reliance on external black box providers. Restricted Data Leasing: Safe, supervised data flow to authorized partners according to times, terms and conditions of your choosing with automated tools for auditing and verification. --- For more information, visit http://bit.ly/2xghY5Y (link is external)
-
Learn more the Audience Center 360, a Google analytic solutions data management platform that helps brands make strong decisions based on a complete understanding of their audience insights, and create relevant and engaging experiences across the entire customer journey. --- For more information visit, http://bit.ly/2xSzX6a (link is external)
-
Blog
Big Data Turns Your TV into Powerful Digital Spy
Simulmedia, Oracle Data Cloud Partnership Aims to Bring Data-Driven Ad Targeting to Linear TV Networks
Targeted TV ad company Simulmedia is partnering with Oracle Data Cloud, a data service company, to target advertisements to consumers based on their in-store purchases. Data-driven advertising is picking up in the linear TV world as cable companies look to cash in on the big data trends that digital platforms base their decisions on already. The data that Oracle Data Cloud is providing via Simulmedia is worth more than $3 trillion in household-level purchase data, according to the announcement (link is external). Simulmedia’s “VAMOS” platform creates data-driven audiences, predicts viewership of the audiences, builds optimized performance-based media plans and reports on media delivery and outcomes. “Bringing Oracle Data Cloud’s purchase-based audiences to national television is a defining moment in the transformation of TV to a data-driven, audience targeted business,” said Dave Morgan, founder and CEO of Simulmedia, in a statement. “By using Simulmedia’s VAMOS platform to precision target Oracle audiences on national TV, brands can align their audience strategies across TV and digital and improve the overall ROI of their advertising spend.” Joe Kyriakoza, vice president-general manager for automotive and TV for Oracle Data Cloud, told MediaPost (link is external)Thursday that this is the first announced partnership in the TV space—though for years the company has already been targeting ads this way in digital. Simulmedia claimed that advertisers will receive an average of between 30% and 100% higher ROI for every campaign. Oracle Data Cloud’s audience numbers quantifying offline transactions are aggregated through data from Oracle’s relationship with Visa Advertising Solutions and DLX Auto audiences, powered by Polk from IHS Markit. Marketers will also be able to deliver ad campaigns to syndicated and custom audience segments from Oracle’s BlueKai Marketplace, as well as onboard their custom CRM and other first-party data. --- For the full article, visit http://bit.ly/2xCxIlD (link is external) -
Blog
Consorting With the Frenemy: Ad Tech Players Partner For Shared Identity Matching
AdWeek article written by James Hercher
Seven independent ad tech companies debuted a programmatic consortium on Thursday that pools their supply- and demand-side cookie IDs into one shared identity asset. The consortium is helmed by AppNexus, MediaMath and LiveRamp, which provides the data matching. Other launch partners include Index Exchange, Rocket Fuel, LiveIntent and OpenX. And it’s a shot across the bow of Facebook and Google, which suck in a majority of digital ad dollars. “The big giants have had an advantage over the open internet in that they have their own deterministic identities for users that allows more precise targeting and cross-device matching,” said AppNexus product VP Patrick McCarthy. Ad tech platforms like AppNexus, Index Exchange and OpenX have the combined online reach marketers want, McCarthy said, but an advertiser must match its data against each platform independently and use LiveRamp to create one-to-one matches. “A universal cookie ID eliminates all the user syncing that goes on between platforms and the lower match rate that necessarily goes with it,” he said. While Google and Facebook have users who contribute deterministic data, the newly formed ad tech consortium can apply first-party data from advertisers and logged-in data from publishers. Marketers and supply sources who are a part of the consortium will access for free the shared cookie pool. LiveRamp’s cross-device graph IdentityLink can be extended to the campaigns, but LiveRamp is still considering commercial terms for ad buyers who want to add a cross-device matching component, company CMO Jeff Smith told AdExchanger. The lack of a unique identifier to date has been one of the biggest factors in fueling concerns around transparency, fairness and control in the digital advertising ecosystem For now, though, any marketer who wants to take advantage of the consortium’s cross-device offering must be a LiveRamp IdentityLink customer. Smith is acutely aware that LiveRamp gains a new business funnel, noting that onboarding potential consortium partners is “definitely is a benefit for us.” “And hopefully the broader benefit is if everyone standardizes around a common identity, the value and efficiency of their marketing will go up,” he added. While the DSPs and SSPs in the consortium may not view it as a new business play, “there certainly will be benefits” that could lead to budget and supply-source consolidation, said MediaMath product VP Philipp Tsipman. For instance, a European video supplier working with MediaMath on a campaign could match its viewers one-to-one with MediaMath’s cookie pool. If that relationship were to occur through the consortium, the match rates would be higher and the profiles would be more robust, since suppliers across the web are contributing data as well. AppNexus’s McCarthy said the system doesn’t cut off buyers from suppliers that don’t use the consortium, but “they will get better matching and better results, so it could naturally funnel more budgets to suppliers that participate.” The market needs “a unique identifier that is neutral,” said OpenX CEO Tim Cadogan in a statement about joining the consortium. “The lack of a unique identifier to date has been one of the biggest factors in fueling concerns around transparency, fairness and control in the digital advertising ecosystem.” --- For the full article, please visit http://bit.ly/2fLZtAB (link is external) -
Blog
Political Scholars, NGOs Call on Facebook, Digital Industry to Support Rules for Political Campaigns
Released on September 22, 2017 at a political microtargeting conference held in Amsterdam, in response to the recent announcement by Facebook and Mark Zuckerberg on changes to how they conduct political ad campaigns. Dear Mark, Your statements on Facebook’s new policies for political advertising were issued as we started a global symposium on micro-targeting in Amsterdam (https://www.ivir.nl/amsterdam-symposium-on-political-micro-targeting/ (link is external)). We are a group of leading international academic experts and civil society representatives from the fields of law, communication, political science and economics who are conducting research on political targeting. Fairness, equality and democratic oversight are key in democratic societies. We appreciate the initiative you have taken and strongly encourage further dialogue and action. Moving this forward we strongly believe that the principles of transparency and disclosure are essential. Facebook should share publicly the full range of paid political contents, disclose the sponsoring actors, and identify the categories of target audiences. This should be done globally as this is an issue that affects elections worldwide. We encourage you and other platforms and actors to join this dialogue to contribute principles for transparency and disclosure. Transparency is a first step in the right direction. Digital political advertising operates in a dynamic tension between data and humans, commerce and politics, power and participation. Some of these tensions can be resolved by transparency, others not. The way forward is to engage with governments, regulators, election monitoring bodies, civil society and academics to develop public policies and guidelines for ensuring fairness, equality, and democratic oversight in digital political campaigns. Can we count on you? Natali Helberger Institute for Information Law (IViR), University of Amsterdam Claes de Vreese Amsterdam School of Communication Research (ASCoR), University of Amsterdam Balazs Bodo Institute for Information Law (IViR), University of Amsterdam Mauricio Moura George Washington University Max von Grafenstein Alexander von Humboldt Institute for Internet and Society, Berlin Jessica Schmeiss Alexander von Humboldt Institute for Internet and Society Sabrina Sassi Universite Laval Tom Dobber Amsterdam School of Communication Research (ASCoR), University of Amsterdam Jeff Chester Center for Digital Democracy, Washington, DC Kathryn Montgomery American University, Washington, DC André Haller Institut für Kommmunikationswissenschaft, Universität Bamberg Damian Tambini Department of Media and Communications, London School of Economics and Political Science Simon Krischinski Johannes Gutenberg Universität Mains Daniel Kreiss School of Media and Journalism, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill -
Digital marketing companies, especially Facebook (link is external) and Google, allied with super-size broadband ISPs (AT&T, Comcast, etc.), defeated (link is external) a bill that would have given Californians the right to have a say in how their digital information can be used. The bill primarily required (link is external) opt-in consent (an informed, informative okay) before our data could be used to help advertisers target us via a home or mobile Internet connection. Google, Facebook, AT&T, Comcast and their partners don’t want individuals to be able to decide for themselves whether they want to be part of these companies’ commercial surveillance system. Working both independently and collectively, the digital marketing businesses can now seamlessly (link is external) gather, analyze and use all our information—whether we are on a mobile device a PC or even watching TV. Our mobile phones and apps send them details of where we go and what we do. All of our “profile” information is collected into a single record, which often contains an ever-growing (link is external) array of other data—about our finances, health, what our kids do, what we view online, where we shop and for what, our race, ethnicity, sexual orientation and more. Google and Facebook use this data to generate massive revenues from advertisers, marketers and political campaigns. AT&T, Comcast, and Verizon have long had “Google envy,” believing that their monopolistic control over the broadband connections most Americans rely on should also shower them with even more financial rewards. That’s why phone and cable companies have scooped (link is external) up digital ad companies, such as Yahoo and AOL. Their vision for the future is to profit significantly by selling us to advertisers when we use our digital devices to stream video, listen to music, play games, etc. The California bill was based on the safeguards that had been enacted by the FCC at the end of the Obama administration, but that President Trump eliminated (link is external) earlier this year and. Google, Facebook and the others knew that if California enacted such consumer safeguards, it would set a powerful precedent. That’s why they engaged in a deceptive (link is external) ad campaign, used their political donations (link is external) for clout with lawmakers, and sent lobbyists to the state to tell tall tales of how Americans have their privacy protected by the FTC. A terrific coalition (link is external) of privacy, consumer, education, children’s advocacy, civil rights and civil liberties group fought for the California bill. We are proud that CDD played a modest role. We will all be back, stronger than ever, when the California state legislature reconvenes next year. But the lesson here is a valuable one and joins the now-almost-daily examples where Google (link is external), Facebook (link is external) and the others misuse their power. The forces of advertising and marketing, now fueled with the ever-growing capabilities of digital applications, undermine the ability of America’s communication and information gatekeepers to effectively serve the public interest. It’s a story that has been repeated throughout the 20th century with the mediums of radio, broadcast television and cable. It’s also always been true of the Internet companies. Protecting our privacy, by stopping these companies from so easily grabbing and monetizing our data, is one way we need to address the problem. The Europeans are about to do precisely (link is external) that—and the U.S. needs to do the same. That’s a very important beginning for what must be a new national agenda protecting the digital rights of all Americans.
-
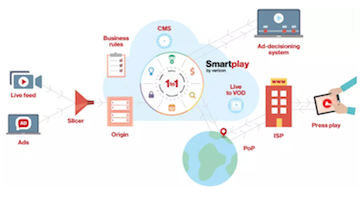
Integrated into their end-to-end platform (link is external), Smartplay provides a real-time, one-to-one connection (link is external) to viewer’s device, enabling them to optimize monetization opportunities. Smartplay’s server-side ad insertion technology (link is external) and industry-standard ad-decisioning system are used to deliver personalized ad experiences across live, linear and on-demand programming. By enforcing advertising business rules according to their monetization strategy, Smartplay enables smarter advertising to help customers get the most value out of their online content. --- For more information, please view the attached PDF and visit http://bit.ly/2w385c7 (link is external).
-
“Marketers. Ready, aim, engage! It is easier than ever to hit the right marketing targets,” explains Equifax (link is external) about its far-reaching data capabilities that capture, analyze, and sell our information. Equifax’s admission last week about its loss of personal information on 143 million Americans—including Social Security and drivers license numbers—is also a wake-up call about the dramatic loss of our privacy in the digital era. Most people think of Equifax as one of the “Big 3” credit-reporting agencies that provide information on our credit worthiness. But Equifax also profits from compiling and selling our data profile to financial services, retail, auto, telecommunications, and other industries for online targeting. As the company itself explains, “Equifax has grown from a consumer credit company into a leading global provider of insights.” It has built a major business offering (link is external) “audience profiling, targeting and measurement tools” that reflect data practices that undermine our privacy and can threaten the interests of consumers. As it explains (link is external) in its “Equifax for Marketing? Absolutely” document, “the advent of Big Data presents nearly limitless potential to help identify the most profitable customers and prospects…. Our data-driven marketing solutions help you synthesize consumer data for a holistic, 360-degree customer view.” Equifax pulls together and “enriches data from disparate sources” so others can have an “enhanced view” of who we are and what we do. Unfortunately, that “enhanced view” means trampling on what should be our right to control who has access and can use our information. We shouldn’t be focused only on the loss of our information from a data breach—but also on how we can better address this issue at its core—by stopping the massive and stealth ways our data are being gathered and used in the first place. Just last month (link is external), Equifax further consolidated (link is external) its “data assets” to create what it calls its “Data-Driven Marketing” suite (DDM). It now provides “a single point of access to all of its data” in order to make using it more convenient for marketers. Equifax’s current business practices reflect how our personal data is traded, shared, and sold today. An array of partners (link is external) collaborate to share information on an individual or a group to be targeted. Data from different sources are gathered, analyzed to identify patterns and opportunities; we are segmented and scored, given an invisible label that describes our financial status and behavior, and that information is then fed into superfast computers that deliver pitches and offers to us via mobile phones, PCs, and connected TVs. In its “Data-driven Marketing Solutions” paper (link is external) on financial services, Equifax touts its ability to directly measure “over $15 trillion of U.S. consumer investable assets…and credit data for over 220 million consumers in the U.S.” Equifax says that it can take that data to help clients target individuals “across channels: email, display, mobile, addressable TV, social, direct mail, point-of-sale, [and] call center.” This is what’s known as “omnichannel” marketing, and involves following us wherever we go online, and, via our mobile phone and apps, into stores and other physical locations as well. For example, Equifax’s IXI (link is external) Services division enables marketers to “differentiate consumer households and neighborhoods, based on wealth, income, spending capacity, share-of-wallet and share of market.” One of its products—AudienceIntel (link is external)—“helps you understand the financial profile of your site visitors…[using] intuitive targeting segments based on our proprietary measures of households’ financial capacity, propensities, preferences, and behavior.” Among IXI’s “digital targeting segments (link is external)” are those who may need a “sub-prime credit card,” a “revolver” (someone with a high balance and will have to accrue interest charges), a “likely student loan target,” and “active debit card users.” Equifax’s IXI promises that it can help guarantee that its clients’ ads have been viewed by their “desired target audience” and whether a sale or some other response was completed—“online or offline.” Unlike Experian and Acxiom, Equifax’s IXI “receives data directly from financial institutions,” which it can segment in a more granular way, according (link is external) to trade reports. Equifax’s “TokenIntel (link is external)” provides retailers with additional insights into our lives by linking point-of-sale and online transaction data with our use of credit cards. This includes geo-location information as well. Although Equifax claims its processes are privacy friendly, the technology it uses enables it to know each consumer and “household, allowing for a clearer picture of a household’s likely value to your brand.” “Communicate with shoppers like you know them…Because You Do!” Equifax explains, urging potential clients to work with it so that “your millions of transaction data points become the foundation” of more profiling and targeting of individuals. Equifax has allied itself with other leading digital data companies that use cutting-edge ad technologies that help target us in milliseconds. They are now working (link is external) with Adobe, Lotame, Salesforce’s Krux, Neustar, MediaMath, and Acxiom’s LiveRamp (link is external), for example (as well as working with music site Pandora (link is external)). In other words, Equifax is helping other data targeting companies gain access to our information—an example of the out-of-control data system unleashed today. Because the U.S. doesn’t have any federal consumer privacy law—rules that the digital data and ad industries are violently opposed to—there’s nothing stopping them from collecting and using even more of our information. The breaches that are occurring begin the very first time a company takes our data, without any legal limits on what that company can do with such information. ---
-
Equifax Inc., a global information solutions provider, today unveiled its next-generation Data-driven Marketing capabilities, designed to help brands conquer the challenges preventing them from realizing their data-driven marketing goals. As marketers across all industries become increasingly reliant on "big data" to help them identify the most profitable customers and prospects and create great experiences, it's clear that marketers need additional help to harness the promise of data-driven marketing. A majority -- 96% -- of marketers report their organizations are attempting to make more central use of customer data, but only 29% are seeing results, according to the IAB's "The Data-Centric Organization (link is external)" whitepaper from September, 2016. Data-driven marketing integrates and enhances the marketing services that Equifax provides. These include credit marketing, IXI Services' wealth-based marketing insights, and digital marketing. This unification enables Equifax to more holistically solve the key challenges that marketing executives face. Leveraging our track record as a trusted data steward and widely-recognized strengths in household economic data, identity and data linking, analytics and technology, Equifax helps brands: Create a single, actionable customer view across data silos and channels; Turn data into an understanding of customer needs and growth opportunities; Engage customers consistently across channels; and Measure results to continuously improve performance and marketing ROI --- For the full article, visit http://bit.ly/2wnuro8 (link is external)
-
Blog
Phone and Cable ISPs Assemble a Big Data Commercial Surveillance Apparatus Aimed at Californians: Use of “hyperlocal” data targeting practices bring greater privacy threats to neighborhoods and communities.
Key control of multiple devices, including TV. ISPs have positioned themselves to expand their consumer data collection across all the devices/platforms they operate. This includes broadband connections (including streaming media), mobile devices, PCs, and also TV. Unlike Google and Facebook, the cable and telephone ISPs largely control the TV set. Comcast has enabled its NBC division to use its set-top (link is external) box data for targeting, for example. Phone and cable companies work with leading data brokers and data marketing “clouds” in order to develop granular and actionable profiles of individuals. This gives ISPs robust understanding of the actions and behaviors of consumers, including financial, health, ethnic, racial, shopping, and even politically related data—all of which is used for personalized targeted marketing. Examples include Comcast (link is external) and Verizon working with Acxiom, among others; Comcast (link is external) and Verizon working with real-time data targeting company MediaMath; Verizon and Comcast (link is external) working with Oracle’s (link is external) marketing cloud division; and Experian (link is external) providing data to Verizon/AOL and AT&T (link is external). ISPs are Identifying and targeting a single consumer across all the devices that person uses—through “cross device identification.” Verizon (which operates both AOL and Yahoo) works with Acxiom’s LiveRamp division. LiveRamp specializes in helping clients fuse together data that allows specific individuals to be identified (link is external) on all their devices, through LiveRamp’s “IdentityLink” LiveRamp matches “PII-based data—like emails, postal addresses, and phone numbers—with…cookies and device IDs….” The company maintains “consistent recognition on 98% of U.S. adults and nearly 100% of U.S. households.” Verizon’s Precision Insights Program is listed as a LiveRamp partner (“the two companies are leveraging the PrecisionID” to give advertisers the ability to run “list-matching” campaigns in mobile, and serve mobile ads to an already built CRM list). AT&T also has a connection with LiveRamp, via its alliance (link is external) for app-based data targeting with Opera Mediaworks. The list of LiveRamp’s data partners is far-reaching, suggesting that Verizon, for example, can acquire extensive data elements on individuals. AT&T has also worked with cross-device targeting specialist Tapad. (link is external) Verizon works with another cross-device company—Drawbridge (link is external)—which also has multiple data-broker partnerships. Phone and cable companies are using set-top box data to also target consumers on their other devices. For example, AT&T recently boasted, “we are now targeting that same consumer across TV and mobile.” ISPs are expanding their use of consumer geolocation data for commercial tracking and ad targeting, creating new privacy threats to neighborhoods and communities. For example, leading geo-tracking company Factual (link is external) is a partner (link is external) with Verizon’s AOL. AT&T (link is external) and Verizon (link is external) also work with geotargeter PlaceIQ. ISPs have been on a data-targeting spending spree to acquire companies that help them target across devices and applications. AT&T has partnered with ad- (and now also data-) giant WPP to own (link is external) a company that helps deliver digital TV and other interactive ads across devices. They are using “verified subscriber identities” to deliver addressable TV and mobile ads, including through apps. Verizon’s acquisition of Yahoo (including Yahoo Finance and Yahoo Mail) gave it control of over 600 million mobile monthly users. Yahoo mail has “225 million logged-in users,” for example, lending valuable scale to AOL’s (link is external) ad-platform business. “Verizon’s subscriber data coupled with Yahoo content and email addresses enables more precise ad targeting,” explained (link is external) one leading publication. ISPs are using their data clout to deliver insight-based targeting. Verizon, for example, promises that it “allows advertisers to pinpoint very specific targets by households." --- -
Blog
Comcast, Cox, Charter Sell Your Data to Political Groups
NCC is owned by cable industry leaders Comcast, Cox and Spectrum, and represents virtually every other multi-channel programming distributor in the US.
What connects cable, online and on demand viewers? NCC Digital Video. NCC’s approach to advertising reaches premium voter audiences across all screens. Only NCC has the unrivaled ability to target authenticated subscribers in a variety of ways across premium cable content and websites. And with our targeting technology, NCC can continue to target this subscriber as well as additional specific audiences throughout the web. NCC A+ Political Advertising gathers first party voter data from all 50 states and offers list matching Premium in-stream video ads run across all screens to an engaged, authenticated audience Dynamic Ad Insertion (DAI) facilitates ad insertion into premium cable programming in OnDemand viewing Premium High Impact Home Page and Sign-In page take overs give maximum brand exposure and impact NCC Political Media is proud of our partnerships with the most reputable research and data sources on US voters. Access to this intelligence allows us to provide you with superior intelligence on how to effectively reach the right voters in your preferred markets, on the best cable networks and online platforms. --- For more information, visit NCCMedia.com -
Deep Root Analytics, a leading media & audience analytics company that creates data platforms for audience targeting and ad monitoring, announced today that it has expanded the number of audiences available with D2 Media Sales to enable political, corporate & advocacy advertisers to target Dish and DIRECTV households using proprietary audience segments. Deep Root Analytics has created 35 new proprietary audience segments based on their affinity scores on political & policy issues and interest in corporate responsibility efforts. These new audiences represent an increase in the Deep Root Analytics footprint to reach Dish & DIRECTV households above their initial announcement (link is external) in 2016 and brings its overall addressable audience offering to more than 60 unique audience segments. As such, Deep Root Analytics has pre-matched these segments to D2’s advertising platform, providing addressable TV advertising to nearly 23 million DIRECTV and DISH satellite households. “In 2017, advocacy and brand advertisers are navigating a tricky and fractured media landscape. They are especially keen to identify and efficiently reach audiences based on what they value and to drive their agenda and manage their brand reputations,” noted Deep Root Analytics CEO Brent McGoldrick. “At Deep Root Analytics, we are focused on helping them make their paid media as data-driven as possible. So, we are thrilled to work with D2 Media Sales and access their best-in-class addressable TV platform to enable our clients to directly communicate with nearly 23 million DIRECTV & DISH customers.” The 35 new proprietary segments created by Deep Root Analytics and made available for addressable advertising via D2 Media Sales include: --- For more information, visit http://bit.ly/2ep1l0U (link is external)
-
Political data firms on both sides of the aisle have bolstered their addressable TV capabilities. Today, Democratic data firm TargetSmart and Republican data outfit Data Trust each announced new partnerships with TV data providers. The outcome should be even more TV spots, especially from congressional campaigns, targeted to households of key voter segments than ever before. Data Trust, the data firm that manages a national voter file for Republicans and right-leaning groups, has partnered with FourthWall Media to match FourthWall's cable viewership data to Data Trust's voter data. The result will be a feed of TV viewer data updated daily and matched against Data Trust's voting history and demographic data. It was a year ago at the Democratic National Committee's summer meeting in Minneapolis when Democratic data firm TargetSmart Communications unveiled the addressable TV and digital ad targeting capabilities it developed with data services firm Experian. Today, TargetSmart expanded its TV data offerings through a partnership with Tru Optik, which provides media consumption data for digital media and connected TV devices such as Roku, Xbox, and smart TVs. The company also has TV data deals with Rentrak and D2 Media Sales, which is a partnership between DISH and DirecTV/AT&T. "We're trying to get as many partnerships out there as possible," said Bill Russell, director of digital partnerships at TargetSmart. These sorts of voter and TV data deals are bringing the targeting capabilities of online advertising to TV ad buys, which historically have resulted in some wasted spending for political campaigns that would do better to target ads to desired voter groups rather than those less likely to support their candidates. The new approaches have grown in popularity following the 2012 election, when President Obama's re-election campaign famously employed innovative data-crunching methods for buying TV ads aimed at voters through programming rarely purchased by political advertisers. By partnering with more and more TV data and media firms, political data companies are bringing what was once accessible only to large statewide or national campaigns to smaller, down-ballot candidates. Through such relationships, political advertisers can reach pre-defined voter segments, such as likely Democratic or Republican voters, or custom groups of voters. --- For the full article, visit http://bit.ly/2wDaz4s (link is external)
-
Reports
Health Wearable Devices Pose New Consumer and Privacy Risks
Lack of Regulation Fostering Unchecked Use of Personal Health Data. Debate over Future of Health Care System Must Address Need for Safeguards.
Personal health wearable devices that consumers are using to monitor their heart rates, sleep patterns, calories, and even stress levels raise new privacy and security risks, according to a report released today by researchers at American University and the Center for Digital Democracy. Watches, fitness bands, and so-called “smart” clothing, linked to apps and mobile devices, are part of a growing “connected-health” system in the U.S., promising to provide people with more efficient ways to manage their own health. But while consumers may think that federal laws will protect their personal health information collected by wearables, the report found that the weak and fragmented health-privacy regulatory system fails to provide adequate safeguards. The report, Health Wearable Devices in the Big Data Era: Ensuring Privacy, Security, and Consumer Protection, provides an overview and analysis of the major features, key players, and trends that are shaping the new consumer-wearable and connected-health marketplace.“Many of these devices are already being integrated into a growing Big Data digital-health and marketing ecosystem, which is focused on gathering and monetizing personal and health data in order to influence consumer behavior,” the report explains. As the use of these devices becomes more widespread, and as their functionalities become increasingly sophisticated, “the extent and nature of data collection will be unprecedented.”The report documents a number of current digital-health marketing practices that threaten the privacy of consumer health information, including “condition targeting,” “look-alike modeling,” predictive analytics, “scoring,” and the real-time buying and selling of individual consumers. The technology of wearable devices makes them particularly powerful tools for data collection and digital marketing. For example, smartphones and other mobile devices already provide access to users’ location information, enabling marketers to target individuals wherever they are, based on analyses of “visitation patterns” and a host of other behavioral and demographic data.The report also explains how an emerging set of techniques and Big-Data practices are being developed to harness the unique capabilities of wearables—such as biosensors that track bodily functions, and “haptic technology” that enables users to “feel” actual body sensations. Pharmaceutical companies are poised to be among the major beneficiaries of wearable marketing.The report offers suggestions for how government, industry, philanthropy, nonprofit organizations, and academic institutions can work together to develop a comprehensive approach to health privacy and consumer protection in the era of Big Data and the Internet of Things. These include:Clear, enforceable standards for both the collection and use of information;Formal processes for assessing the benefits and risks of data use; andStronger regulation of direct-to-consumer marketing by pharmaceutical companies.“The connected-health system is still in an early, fluid stage of development,” explained Kathryn C. Montgomery, PhD, professor at American University and a co-author of the report. “There is an urgent need to build meaningful, effective, and enforceable safeguards into its foundation.”Such efforts “will require moving beyond the traditional focus on protecting individual privacy, and extending safeguards to cover a range of broader societal goals, such as ensuring fairness, preventing discrimination, and promoting equity,” the report says.“In the wake of the recent election, the United States is on the eve of a major public debate over the future of its health-care system,” the report notes. “The potential of personal digital devices to reduce health-care spending will likely play an important role,” as lawmakers deliberate the fate of the Affordable Care Act. However, unless there are adequate regulatory safeguards in place, “consumers and patients could face serious risks to their privacy and security, and also be subjected to discrimination and other harms.”“Americans now face a growing loss of their most sensitive information, as their health data are collected and analyzed on a continuous basis, combined with information about their finances, ethnicity, location, and online and off-line behaviors,” said Jeff Chester, Executive Director of the Center for Digital Democracy, and another co-author of the report. “Policy makers must act decisively to protect consumers in today’s Big Data era.”The Robert Wood Johnson Foundation provided funding for the report.The three authors of the report —Kathryn Montgomery, Jeff Chester, and Katharina Kopp—have played a leading role on digital privacy issues, and were responsible for the campaign during the 1990s that led to enactment by Congress of the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA).---Full report attached.Kathryn Montgomery, Jeff Chester, Katharina Kopp -
Blog
New Report: Health Wearable Devices Pose New Consumer and Privacy Risks
Lack of Regulation Fostering Unchecked Use of Personal Health Data. Debate over Future of Health Care System Must Address Need for Safeguards.
Personal health wearable devices that consumers are using to monitor their heart rates, sleep patterns, calories, and even stress levels raise new privacy and security risks, according to a report released today by researchers at American University and the Center for Digital Democracy. Watches, fitness bands, and so-called “smart” clothing, linked to apps and mobile devices, are part of a growing “connected-health” system in the U.S., promising to provide people with more efficient ways to manage their own health. But while consumers may think that federal laws will protect their personal health information collected by wearables, the report found that the weak and fragmented health-privacy regulatory system fails to provide adequate safeguards. The report, Health Wearable Devices in the Big Data Era: Ensuring Privacy, Security, and Consumer Protection, provides an overview and analysis of the major features, key players, and trends that are shaping the new consumer-wearable and connected-health marketplace.“Many of these devices are already being integrated into a growing Big Data digital-health and marketing ecosystem, which is focused on gathering and monetizing personal and health data in order to influence consumer behavior,” the report explains. As the use of these devices becomes more widespread, and as their functionalities become increasingly sophisticated, “the extent and nature of data collection will be unprecedented.”The report documents a number of current digital-health marketing practices that threaten the privacy of consumer health information, including “condition targeting,” “look-alike modeling,” predictive analytics, “scoring,” and the real-time buying and selling of individual consumers. The technology of wearable devices makes them particularly powerful tools for data collection and digital marketing. For example, smartphones and other mobile devices already provide access to users’ location information, enabling marketers to target individuals wherever they are, based on analyses of “visitation patterns” and a host of other behavioral and demographic data.The report also explains how an emerging set of techniques and Big-Data practices are being developed to harness the unique capabilities of wearables—such as biosensors that track bodily functions, and “haptic technology” that enables users to “feel” actual body sensations. Pharmaceutical companies are poised to be among the major beneficiaries of wearable marketing.The report offers suggestions for how government, industry, philanthropy, nonprofit organizations, and academic institutions can work together to develop a comprehensive approach to health privacy and consumer protection in the era of Big Data and the Internet of Things. These include:Clear, enforceable standards for both the collection and use of information;Formal processes for assessing the benefits and risks of data use; andStronger regulation of direct-to-consumer marketing by pharmaceutical companies.“The connected-health system is still in an early, fluid stage of development,” explained Kathryn C. Montgomery, PhD, professor at American University and a co-author of the report. “There is an urgent need to build meaningful, effective, and enforceable safeguards into its foundation.”Such efforts “will require moving beyond the traditional focus on protecting individual privacy, and extending safeguards to cover a range of broader societal goals, such as ensuring fairness, preventing discrimination, and promoting equity,” the report says.“In the wake of the recent election, the United States is on the eve of a major public debate over the future of its health-care system,” the report notes. “The potential of personal digital devices to reduce health-care spending will likely play an important role,” as lawmakers deliberate the fate of the Affordable Care Act. However, unless there are adequate regulatory safeguards in place, “consumers and patients could face serious risks to their privacy and security, and also be subjected to discrimination and other harms.”“Americans now face a growing loss of their most sensitive information, as their health data are collected and analyzed on a continuous basis, combined with information about their finances, ethnicity, location, and online and off-line behaviors,” said Jeff Chester, Executive Director of the Center for Digital Democracy, and another co-author of the report. “Policy makers must act decisively to protect consumers in today’s Big Data era.”The Robert Wood Johnson Foundation provided funding for the report.The three authors of the report —Kathryn Montgomery, Jeff Chester, and Katharina Kopp—have played a leading role on digital privacy issues, and were responsible for the campaign during the 1990s that led to enactment by Congress of the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA).---Full report attached.